Net/Gross Area Surveys
Highway Surveys
NIA Survey uses
GIA Survey uses
RICS Practice
Gross External Area Surveys
Retail Zoning
IPM uses
Area surveys and referencing reports are typically prepared by land surveyors and are used to determine and document the precise measurements, boundaries, and features of a particular area of land. These reports are commonly required for various purposes, including land development, property transactions, construction projects, and legal disputes.
Area surveys involve the physical measurement of a piece of land using specialised surveying instruments and techniques. Surveyors use equipment such as total stations, GPS receivers, and laser scanners to accurately measure distances, angles, and elevations on the ground. They may also employ aerial surveying techniques using drones or aircraft for larger areas.
The collected data is then processed, analysed, and compiled into an area survey report This report provides a detailed description of the land’s boundaries, dimensions, topography, and any other relevant features. It may include maps, plans, and diagrams that illustrate the surveyed area, along with numerical data and written descriptions.
Referencing reports, on the other hand, focus on establishing, the relationship between a specific piece of land and adjacent properties or known reference points. These reports help identify the exact location of a property within a larger geographical context. They typically involve researching and analysing land records, historical maps, legal descriptions, and other relevant documents to establish the boundaries and spatial relationships of the surveyed land.
Referencing reports often include information about adjoining properties, easements, rights of way, encroachments, and other factors that may impact the surveyed area. These reports are crucial for ensuring accurate land ownership, resolving property disputes, and providing a comprehensive understanding of the land’s context and history.
Overall, area surveys and referencing reports play a vital role in land management, real estate transactions, urban planning, and various other fields that require precise information about the physical characteristics and legal aspects of a piece of land.
Net and gross internal area surveys and reports are conducted to determine and document the usable floor space within a building or structure. These surveys provide valuable information about the size and layout of the internal areas, which is important for various purposes such as space planning, leasing, valuation, and compliance with building regulations.
Net Internal Area (NIA) refers to the total usable floor area within a building, excluding any non-habitable spaces such as corridors, stairwells, mechanical rooms, and walls. NIA represents the actual space available for occupancy, use or lease within the building.
During a net internal area survey, a surveyor measures the internal dimensions of each room or area within a building, taking into account the internal walls and features. They typically use measuring tapes or laser distance meters to obtain accurate measurements. The collected measurements are then used to calculate the internal area of the building.
Gross Internal Area (GIA), on the other hand, includes all the useable floor spaces within a building, including the NIA as well as the non-habitable spaces such as corridors, stairwells, and mechanical rooms. GIA represents the total floor area contained within the building’s perimeter walls.
In a gross internal area survey, the surveyor measures the internal dimensions of all areas, including both usable and non-usable spaces. This includes the thickness of walls, partitions, and other features that may impact the total floor area. The measurements are then used to calculate the total gross internal area of the building.
The survey results are typically compiled into a report that gives detailed information about the measured areas, calculations, and floor plans. The report may also include graphical representations, such as floor plan drawings or diagrams, to illustrate the layout and dimensions of the usable floor space within a building.
NIA surveys, or Net Internal Area surveys, are conducted to determine the usable floor space within a building, excluding non-habitable areas such as corridors, stairwells, and mechanical rooms. These surveys are important for various purposes, including space planning, leasing, valuation, and compliance with building regulations.
During NIA surveys, a surveyor measures the internal dimensions of each room or area within the building. They typically use measurements tapes or laser distances meters to obtain accurate measurements of the floor areas. The surveyor takes into account the internal walls and features to determine the net usable area of each space.
The measurements collected during the survey are used to calculate the total net area of the building. This calculation involves summing up the areas of all the usable spaces within the building, while excluding non-habitable building areas. The NIA represents the actual floor space available for occupancy, use, or lease within the building.
The results of the NIA survey are typically compiled into a report. This report provides detailed information about the measured areas, calculations, and floor plans. It may include a breakdown of the net internal areas for each room or space within the building. Additionally, the report may contain graphical representations, such as floor plan drawings or diagrams, to illustrate the layout and dimensions of the internal areas.
NIA surveys are valuable for various stakeholders involved in the management, utilizations, or valuation of a building. Property owners, real estate agents, developers, and tenants rely on NIA information for lease negotiations, space planning, and understanding the usable area of a property. Additionally, NIA surveys are often required to comply with building regulations and standards that dictate the minimum floor area requirements for different types of spaces.
Overall, NIA surveys provide essential information about the net usable floor space within a building, allowing stakeholders to make informed decisions regarding space utilisation, leasing, and compliance with regulations.
A Net Internal Area (Nia) survey is a type of survey conducted to measure and determine the usable floor space within a building, excluding non-habitable areas such as corridors, stairwells, and mechanical rooms. The primary purpose of an NIA survey is to provide an accurate assessment of the actual floor space available for occupancy, use, or lease within a building.
During an NIA survey, a surveyor measures the internal dimensions of each room or area within the building. This typically involves measuring a length and width of each space, taking into account any internal walls, columns, or features that may affect the usable floor area. The surveyor may use measuring tapes, laser distance meters, or other specialised tools to obtain measurements.
The collected measurements are then used to calculate the total NIA of the building. The calculation involves summing up the areas of all the usable spaces while excluding non-habitable areas. The resulting NIA represents the net internal floor space available for various activities such as office work, commercial use, or other specific purposes.
NIA surveys are used for a variety of purposes, including:
Overall, NIA surveys provide crucial information about the net usable floor space within a building, enabling stakeholders to make informed decisions regarding space utilization, leasing, valuation, and compliance with regulations.
Understanding Area Reference Surveys
Area reference surveys involve the use of specialist surveying equipment, such as GPS trackers, laser scanners, and even drones, to accurately measure a property or piece of land. During an area reference survey, a surveyor will conduct a comprehensive property analysis that incorporates physical measurements of the space, including angles and elevations, as well as referencing reports that establish that property’s location in relation to nearby reference points. They may also conduct an area measurement survey which establishes clear property boundaries.
A detailed area reference survey will typically consider a variety of different area calculations, including –
Determines the usable floor space in a building, excluding non-habitable areas like corridors and stairwells.
Determines the total floor space within a building, including non-habitable areas.
Determines the total floor space of a building, including the external walls.
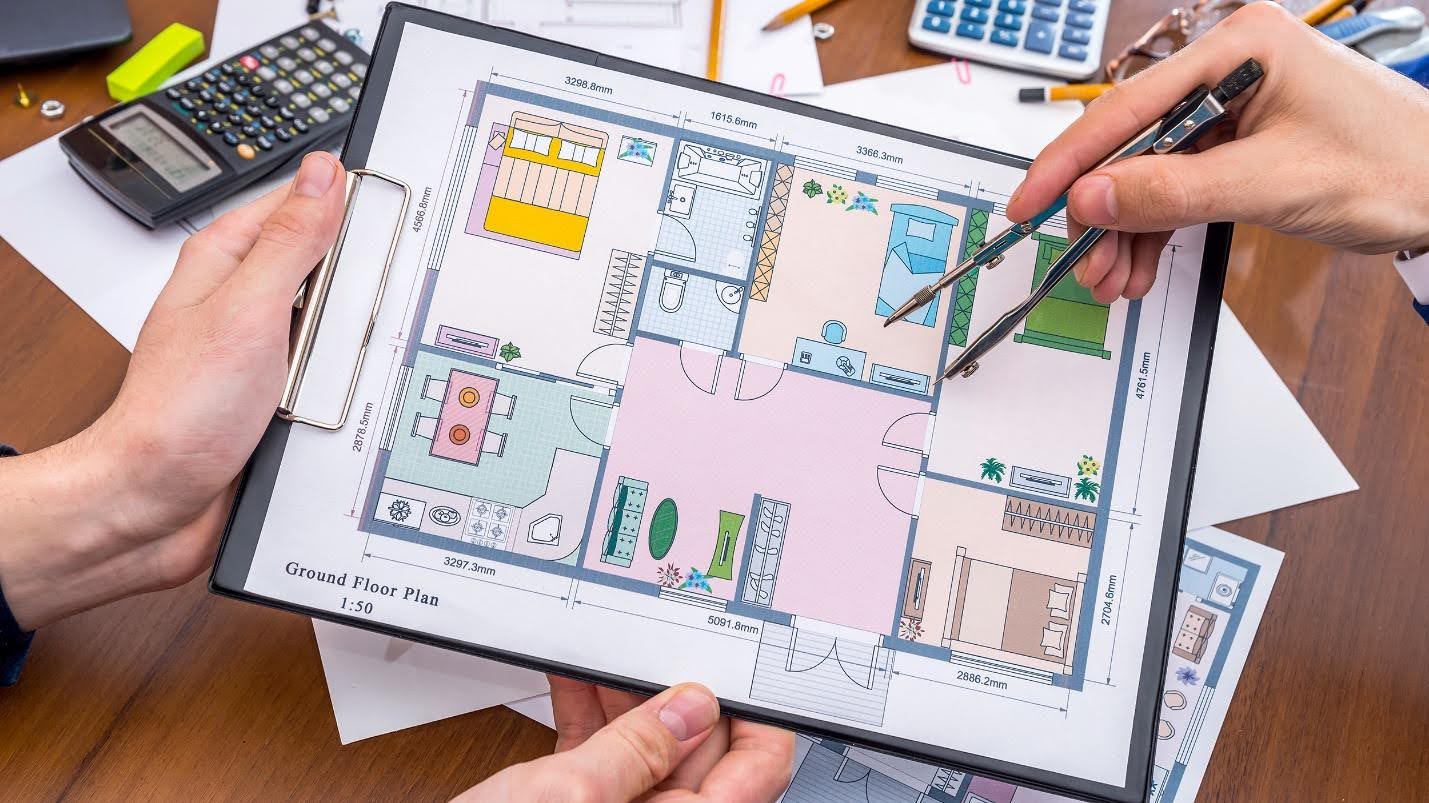
These property area measurements play a key role in accurately documenting a property’s size, boundaries, and location, and can prove valuable for sales and acquisitions, as well as property valuation, compliance, and leasing amongst other purposes.
While area reference surveys apply to a broad range of industries, they hold particular relevance within real estate, construction, and property management where accuracy and compliance are key to project success and profit turnovers.
A Gross Internal Area (GIA) survey is a type of survey conducted to measure and determine the total usable floor space within a building, including both the net usable areas and non-habitable spaces such as corridors, stairwells, and mechanical rooms. The primary purpose of a GIA survey is to provide an accurate assessment of the total floor area contained within the building’s perimeter walls.
During a GIA survey, a surveyor measures the internal dimensions of all areas within the building, including both usable and non-usable spaces. This involves measuring the length and width of each room or area, considering the internal walls, columns, and other features that may impact the total floor area. The surveyor may use measuring tapes, laser distance meters, or other specialised tools to obtain precises measurements.
The collected measurements are then used to calculate the total GIA of the building. The calculation involves summing up the areas of all the measured spaces, including the net internal areas and non-habitable areas. The resulting GIA represents the total floor area contained within the building’s perimeter walls.
GIA surveys are used for various purposes, including:
In summary, GIA surveys provide crucial information about the total usable floor space within a building, including both net internal areas and non-usable spaces. They are used for property valuation, space planning, compliance with regulations, lease negotiations, and property management. GIA data helps stakeholders make informed decisions and ensure efficient utilisation of building space.
The RICS 6th Code of Measuring Practice, published by the Royal Institution of Chartered Surveyors (RICS), is a professional standard that provides guidelines for measuring and calculating the size and dimensions of buildings. The code is primarily used in the United Kingdom and is applicable to various sectors, including real estate, construction, property management, and valuation.
The 6th Code of Measuring Practice serves as a comprehensive framework for consistent and accurate measurement practices within the industry. It covers various aspects of building measurement, including terminology, measurement methodologies, and standards for different types of properties.
Key features and topics covered in the RICS 6TH Code of Measuring Practice include:
The RICS 6th Code of Measuring Practice is an important reference document for professionals involved in the measurement, valuation, and management of buildings. It promotes consistency, accuracy, and transparency in building measurement practices, ensuring that stakeholders have a common understanding of the size and dimensions of properties.
It’s worth noting that the RICS periodically updates its codes and standards to reflect changes in industry practices and advancements in technology. Therefore, it is essential to consult the most recent version of the RICS Code of Measuring Practice for the most up to date guidelines and standards.
Gross External Area (GEA) surveys are conducted to measure and determine the total floor area of a building, including all external walls. The GEA includes both the internal usable space and the thickness of external walls, providing a comprehensive measurement of the building’s total footprint.
During a GEA survey, a surveyor measures the external dimensions of the building, including the length, width, and height of external walls. This involves measuring the external surfaces the walls, excluding any projections such as balconies, canopies, or external stairs. The surveyor may use measuring tapes, laser distance meters, or other tools to obtain accurate measurements.
The collected measurements are then used to calculate the total GEA of the building. The calculation includes summing up the areas of all the floors, including the external walls/ The resulting GEA represents the total floor area contained within the external boundaries of the building.
GEA surveys are used for various purposes, including:
GEA surveys provide a comprehensive measurement of a building’s floor area, including the external walls, and are used by various stakeholders in the real estate and construction industries. They play a crucial role in property valuation, planning, compliance with regulations, lease agreements, and asset management.
Retail Zoning, specifically Inferred Total Zone Area (ITZA), is a concept used in the retail industry to measure and allocate space within a retail store based on its commercial zoning. ITZA is a method of calculating the usable sales floor area within a store, taking into account the specific merchandising zones and departments.
The ITZA approach recognises that different zones or departments within a retail store have varying sales densities and profitability. By allocating space based on these factors, retailers can optimize the use of their floor area and improve overall store performance.
Here’s an overview of how ITZA works:
The ITZA approach helps retailers optimise their store layouts, product displays, and overall space utilisation. By allocating more space to high preforming zones and optimising the arrangement of merchandise, retailers can enhance the customer experience, maximise sales potential, and improve profitability.
It’s important to note that ITZA is just one of the methods used in retail space allocation and zoning. Other approaches such as Gross Leasable Area (GLA) or Net Leasable Area (NLA), may also be employed, depending on the specific needs and objectives of the retailed and the industry standards in a particular region.
Overall, ITZA provides a framework for retailers to strategically allocate space within their stores based on sales density and profitability, enabling them to optimise their retail environments and enhance business performance.
Area reference surveys are becoming increasingly vital to ensuring compliance with IPMS (International Property Measurement Standards).
This international set of open-source standards for measuring buildings was initially developed by a range of professional bodies including the Royal Institution of Chartered Surveyors (RICS) to create consistent standards across the commercial real estate industry.
The first phase of the project was ‘IPMS for offices’ in 2014, but the more recent ‘IPMS: all buildings’ applies to everything from barns to high-end apartments. The IPMS now includes 8 standards in total, which relate to things like the intended use or location of a property. The overall objectives of IPMS include:
Broadly, IPMS adoption promotes a more reliable real estate industry and facilitates informed decision-making and easily understandable industry consistency. IPMS-compliant measurements via a professional area reference survey can provide transparency, comparability and trust in property data, even if you’re selling, leasing or buying across unfamiliar international markets.
In the mind of IPMS compliance, area reference surveys apply to a wide range of industries and uses, particularly within the real estate sphere. Prime real-world examples of when an area reference survey might be necessary include –
Area reference surveys are key to property sales and leasing, both of which rely on accurate area calculations to ensure fair pricing or reliable rental agreements. Landlords could also benefit from area reference surveys that ensure compliance with licensing regulations like minimum size requirements.
Architects and planners can use precise area data to ensure they’re effectively utilising available space during remodelling or new building projects. Measurement surveys can also ensure legally compliant projects that sit comfortably within land boundaries.
An area reference report will provide reliable measurement figures that ensure accuracy and maximum profits across property appraisals and valuations. Area surveys can also help to inform accurate and cost-effective taxation, business rates, and insurance appraisals in commercial or residential spaces.
Area surveys can prove useful for facilities management, which involves ongoing optimisation and planning within a property project. Property managers and landlords, in particular, can use area surveys to conduct occupancy assessments, create compliant safety plans, and so on.
What to Expect From An Area Reference Survey
Area reference surveys apply to a wide range of industries and we pride ourselves in offering fully tailored solutions here at Castle Surveys Ltd. Just a few deliverables you can expect from our area reference surveys include –
Whether you’re leasing, selling, or developing a property, accuracy is essential for both legal and technical purposes. We ensure peace of mind for each of our stakeholders by providing a guaranteed certification of measurement accuracy, which is backed by cutting-edge technology and fully trained surveying professionals.
Area reference surveys are essential for adherence to industry standards and compliance across the board, meaning that you can’t afford to risk unreliable findings. Put your doubts to bed when you choose trustworthy area surveys with Castle Surveys Ltd.
Our fully trained team has specialist expertise in delivering IPMS-compliant area surveys for diverse property types including commercial and residential premises, as well as properties that you’re preparing to buy, sell, or lease on international markets.
We utilise our advanced surveying equipment and technology within area survey and measurement report we conduct and will provide you with a reliable, easy-to-understand report, complete with verifiable data and scalable CAD drawings of our findings.
Whether you’re looking to create detailed project plans, or you simply want to solve a boundary dispute, our team will work quickly and efficiently to get the job done. Simply get in touch to discuss your needs today.